|
Herniated cervical intervertebralp discs with radiculopathy: an outcome study of conservatively or surgically treated patients. |
Kategoriarkiv: Head
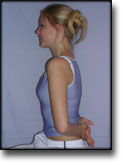
step4
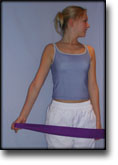
Training ladder for:
MUSCLE INFILTRATIONS IN THE NECK/SHOULDER
(MYOSER)
STEP 4 |
Unlimited: Cycling. Swimming. Running.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
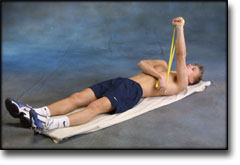
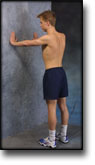
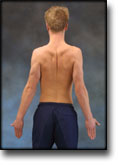
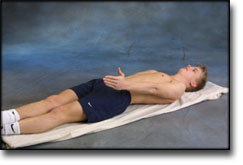
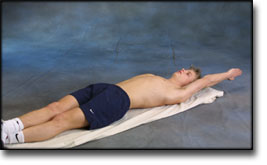
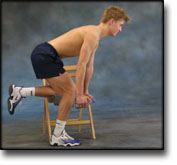
Stretching is carried out in the following way: stretch the muscle group for 3-5 seconds. Relax for 3-5 seconds. The muscle group should subsequently be stretched for 20 seconds. The muscle is allowed to be tender, but must not hurt. Relax for 20 seconds, after which the procedure can be repeated. The time consumed for stretching, coordination and strength training can be altered depending on the training opportunities available and individual requirements. |
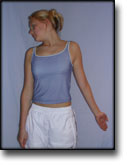
step3
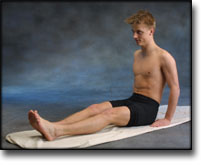
Training ladder for:
MUSCLE INFILTRATIONS IN THE NECK/SHOULDER
(MYOSER)
STEP 3 |
Unlimited: Cycling. Swimming. Running.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Stretching is carried out in the following way: stretch the muscle group for 3-5 seconds. Relax for 3-5 seconds. The muscle group should subsequently be stretched for 20 seconds. The muscle is allowed to be tender, but must not hurt. Relax for 20 seconds, after which the procedure can be repeated. The time consumed for stretching, coordination and strength training can be altered depending on the training opportunities available and individual requirements. |
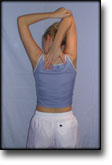
step2
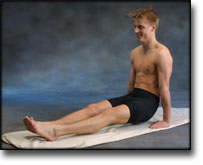
Training ladder for:
MUSCLE INFILTRATIONS IN THE NECK/SHOULDER
(MYOSER)
STEP 2 |
Unlimited: Cycling. Swimming. Running.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Stretching is carried out in the following way: stretch the muscle group for 3-5 seconds. Relax for 3-5 seconds. The muscle group should subsequently be stretched for 20 seconds. The muscle is allowed to be tender, but must not hurt. Relax for 20 seconds, after which the procedure can be repeated. The time consumed for stretching, coordination and strength training can be altered depending on the training opportunities available and individual requirements. |
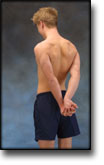
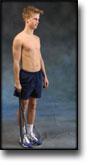
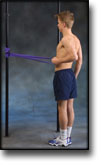
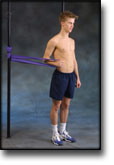
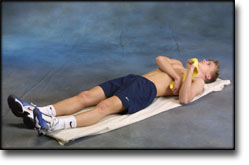
step1
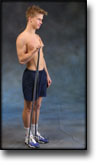
Training ladder for:
MUSCLE INFILTRATIONS IN THE NECK/SHOULDER
(MYOSER)
STEP 1 |
| The indications of time after stretching, coordination training and strength training show the division of time for the respective type of training when training for a period of one hour. The time indications are therefore not a definition of the daily training needs, as the daily training is determined on an individual basis.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Stretching is carried out in the following way: stretch the muscle group for 3-5 seconds. Relax for 3-5 seconds. The muscle group should subsequently be stretched for 20 seconds. The muscle is allowed to be tender, but must not hurt. Relax for 20 seconds, after which the procedure can be repeated. The time consumed for stretching, coordination and strength training can be altered depending on the training opportunities available and individual requirements. |
treatment-article4
|
Active neck muscle training in the treatment of chronic neck pain in women: a randomized controlled trial. |
treatment-article3
|
Treatment of myofascial trigger-points with ultrasound combined with massage and exercise–a randomised controlled trial. |
treatment-article2
|
Rehabilitation of neck-shoulder pain in women industrial workers: a randomized trial comparing isometric shoulder endurance training with isometric shoulder strength training. DESIGN. SETTING. INTERVENTION. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES. RESULTS. CONCLUSIONS. |
treatment-article1
|
Perceived pain before and after three exercise programs–a controlled clinical trial of women with work-related trapeziusP myalgia. |
bandage-article2
|
The incidence of sports-related facial trauma in children. |