


|
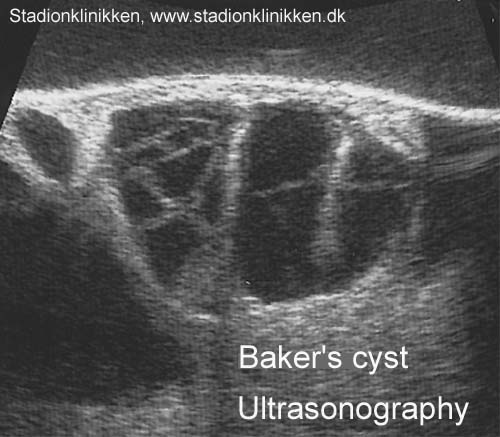
Placement of intra-articular injections verified by ultrasonography and injected air as contrast medium. |
|
“Dem bones”: osteochondral injuries of the knee. |
|
Results of reconstruction of acute ruptures of the anterior cruciate ligament with an iliotibial band autograft. |
|
Revision ACL reconstruction using autogenous patellar tendon graft. |
Training ladder for:
RUPTURE OF THE ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT
(RUPTURA LIGAMENTUM CRUCIATUM ANTERIUS)
| The following exercises can only be considered as a supplement to the guidelines furnished by the doctor which performed the operation. Specific precautions are necessary as the operation can be complicated. The training must not bring about swelling or pain in the knee. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unlimited: Cycling. Swimming. Running.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Stretching is carried out in the following way: stretch the muscle group for 3-5 seconds. Relax for 3-5 seconds. The muscle group should subsequently be stretched for 20 seconds. The muscle is allowed to be tender, but must not hurt. Relax for 20 seconds, after which the procedure can be repeated. The time consumed for stretching, coordination and strength training can be altered depending on the training opportunities available and individual requirements. |
Training ladder for:
RUPTURE OF THE ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT
(RUPTURA LIGAMENTUM CRUCIATUM ANTERIUS)
| The following exercises can only be considered as a supplement to the guidelines furnished by the doctor which performed the operation. Specific precautions are necessary as the operation can be complicated. The training must not bring about swelling or pain in the knee. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cycling with raised saddle. Swimming (Backstroke). Light jogging.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Stretching is carried out in the following way: stretch the muscle group for 3-5 seconds. Relax for 3-5 seconds. The muscle group should subsequently be stretched for 20 seconds. The muscle is allowed to be tender, but must not hurt. Relax for 20 seconds, after which the procedure can be repeated. The time consumed for stretching, coordination and strength training can be altered depending on the training opportunities available and individual requirements. |
Training ladder for:
RUPTURE OF THE ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT
(RUPTURA LIGAMENTUM CRUCIATUM ANTERIUS)
| The following exercises can only be considered as a supplement to the guidelines furnished by the doctor which performed the operation. Specific precautions are necessary as the operation can be complicated. The training must not bring about swelling or pain in the knee. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unlimited: Cycling with raised saddle. Swimming (Backstroke). Running in deep water.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Stretching is carried out in the following way: stretch the muscle group for 3-5 seconds. Relax for 3-5 seconds. The muscle group should subsequently be stretched for 20 seconds. The muscle is allowed to be tender, but must not hurt. Relax for 20 seconds, after which the procedure can be repeated. The time consumed for stretching, coordination and strength training can be altered depending on the training opportunities available and individual requirements. |
Training ladder for:
RUPTURE OF THE ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT
(RUPTURA LIGAMENTUM CRUCIATUM ANTERIUS)
| The following exercises can only be considered as a supplement to the guidelines furnished by the doctor which performed the operation. Specific precautions are necessary as the operation can be complicated. The training must not bring about swelling or pain in the knee. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unlimited: Cycling with raised saddle. Swimming (Backstroke). Running in deep water.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Stretching is carried out in the following way: stretch the muscle group for 3-5 seconds. Relax for 3-5 seconds. The muscle group should subsequently be stretched for 20 seconds. The muscle is allowed to be tender, but must not hurt. Relax for 20 seconds, after which the procedure can be repeated. The time consumed for stretching, coordination and strength training can be altered depending on the training opportunities available and individual requirements. |
Training ladder for:
RUPTURE OF THE ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT
(RUPTURA LIGAMENTUM CRUCIATUM ANTERIUS)
| The following exercises can only be considered as a supplement to the guidelines furnished by the doctor which performed the operation. Specific precautions are necessary as the operation can be complicated. The training must not bring about swelling or pain in the knee. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unlimited: Swimming (Backstroke). Running in deep water.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Stretching is carried out in the following way: stretch the muscle group for 3-5 seconds. Relax for 3-5 seconds. The muscle group should subsequently be stretched for 20 seconds. The muscle is allowed to be tender, but must not hurt. Relax for 20 seconds, after which the procedure can be repeated. The time consumed for stretching, coordination and strength training can be altered depending on the training opportunities available and individual requirements. |