|
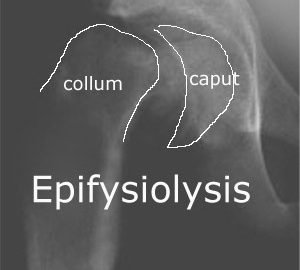
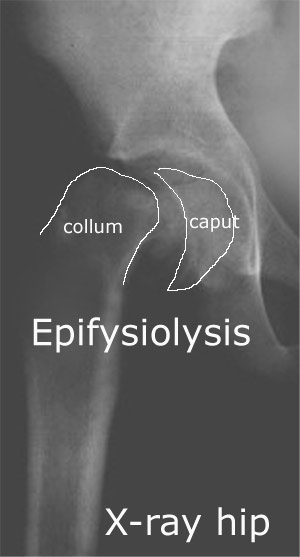
Osteonecrosis of the femoral head associated with slipped capital femoral epiphysis. Kennedy JG, Hresko MT, Kasser JR, Shrock KB, Zurakowski D, Waters PM, Millis MB. J Pediatr Orthop 2001 Mar-Apr;21(2):189-93 |

|
Osteonecrosis of the femoral head associated with slipped capital femoral epiphysis. Kennedy JG, Hresko MT, Kasser JR, Shrock KB, Zurakowski D, Waters PM, Millis MB. J Pediatr Orthop 2001 Mar-Apr;21(2):189-93 |
|
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis: evaluation of different modes of treatment. Rostoucher P, Bensahel H, Pennecot GF, Kaewpornsawan K, Mazda K. J Pediatr Orthop B 1996 Spring;5(2):96-101 |
|
Diagnostic imaging of the early slipped capital femoral epiphysis. Magnano GM, Lucigrai G, De Filippi C, Castriota Scanderberg A, Pacciani E, Toma P. Radiol Med (Torino) 1998 Jan-Feb;95(1-2):16-20 |