|
Ultrasonography as a tool for diagnosis, guidance of local steroid injection and, together with pressure algometry, monitoring of the treatment of athletes with chronic jumper’s knee and Achilles tendinitis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.
Fredberg U, Bolvig L, Pfeiffer-Jensen M, Clemmensen D, Jakobsen BW, Stengaard-Pedersen K. Scand J Rheumatol. 2004;33(2):94-101.
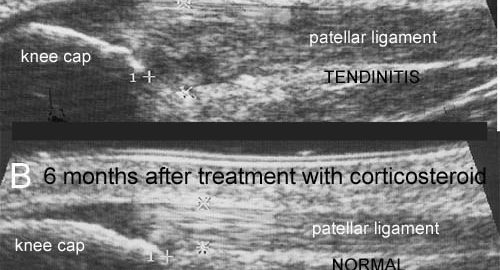
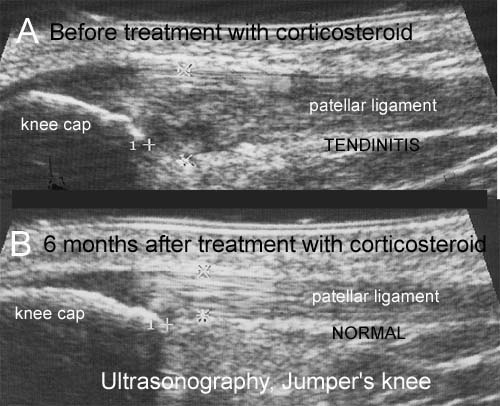
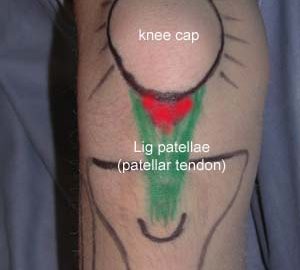
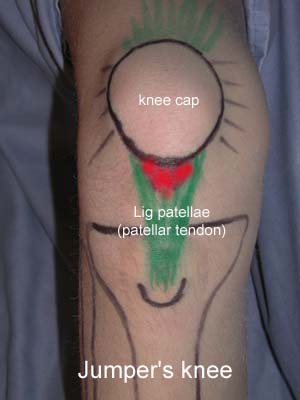
BACKGROUND: The diagnosis of Achilles and patella tendinitis has until recently been based on clinical examination, and treatment with local steroid injection has been given blindly. This is the first randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled study of local steroid injection in athletes with chronic tendinitis, which used ultrasonography to increase diagnostic accuracy, to guide the correct placement of local steroid and, conjunctively with pressure algometry, to objectify and monitor the results of treatment. METHOD: Forty-eight athletes each with severe symptomatic tendinitis of a patellar (24) or Achilles tendon (24) for more than 6 months, whose conditions were confirmed ultrasonographically, and who all failed conservative treatment (rehabilitation) were included in this double-blind, placebo-controlled study and treated with three ultrasonographically guided peritendinous injections of steroid or placebo. RESULTS: The conditions of only one-third of the referred athletes with clinically suspected tendinitis were confirmed by ultrasonographic examination. The ultrasonographically guided peritendinous injection of steroid had a significant effect in reducing pain and thickening of tendons. CONCLUSION: Ultrasonography should be used in the future to assure precise diagnosis and to guide the peritendinous injection of steroid in chronic Achilles and patella tendinitis. Ultrasonography and pressure algometry are recommended as objective methods for monitoring the effect of treatment. Ultrasonographically guided injection of long-acting steroid can normalize the ultrasonographic pathological lesions in the Achilles and patellar tendons, and has a dramatic clinical effect but when combined with aggressive rehabilitation with running after a few days, many will have relapse of symptoms within 6 months (see the article – 1,5 mb).
|