|
Sensitivity of a clinical examination to predict need for radiography in children with ankle injuries: a prospective study.
Boutis K, Komar L, Jaramillo D, Babyn P, Alman B, Snyder B, Mandl KD, Schuh S. Lancet 2001 Dec 22-29;358(9299):2118-21
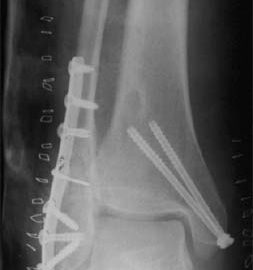
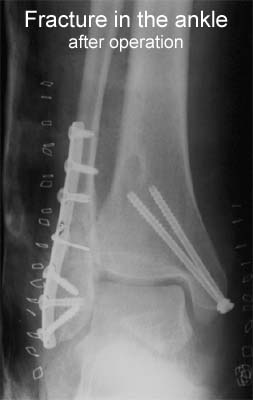
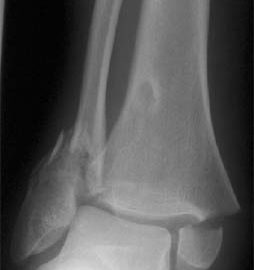
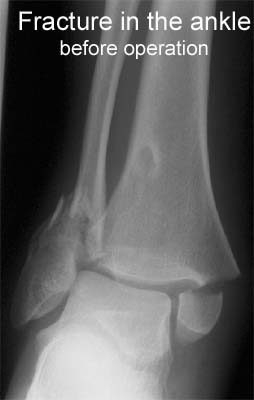
BACKGROUND: Radiographs are ordered routinely for children with ankle trauma. We assessed the predictive value of a clinical examination to identify a predefined group of low-risk injuries, management of which would not be affected by absence of a radiograph. We aimed to show that no more than 1% of children with low-risk examinations (signs restricted to the distal fibula) would have high-risk fractures (all fractures except avulsion, buckle, and non-displaced Salter-Harris I and II fractures of the distal fibula), and to compare the potential reduction in radiography in children with low-risk examinations with that obtained by application of the Ottawa ankle rules (OAR). METHODS: Standard clinical examinations and subsequent radiographs were prospectively and independently evaluated in two tertiary-care paediatric emergency departments in North America. Eligible participants were healthy children aged 3-16 years with acute ankle injuries. Sample size, negative and positive predictive values, sensitivity, and specificity were calculated. McNemar’s test was used to compare differences in the potential reduction in radiographs between the low-risk examination and the OAR. FINDINGS: 607 children were enrolled; 581 (95.7%) received follow-up. None of the 381 children with low-risk examinations had a high-risk fracture (negative predictive value 100% [95% CI 99.2-100]; sensitivity 100% [93.3-100]). Radiographs could be omitted in 62.8% of children with low-risk examinations, compared with only 12.0% reduction obtained by application of the OAR (p<0.0001). INTERPRETATION: A low-risk clinical examination in children with ankle injuries identifies 100% of high-risk diagnoses and may result in greater reduction of radiographic referrals than the OAR.
|