MUSCULAR BLEEDING ON THE UPPER ARM
|
||
|
||
|
||
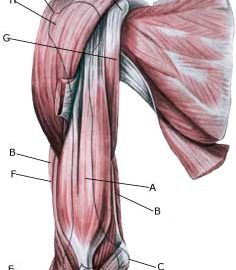
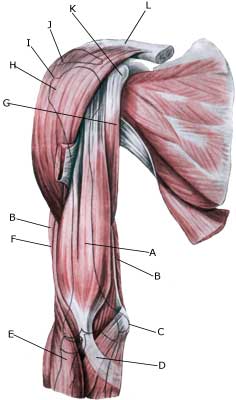
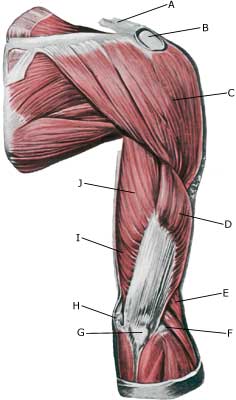
| Cause: If a muscle is subjected to a blow the muscle belly, which contains blood vessels, is pressed against the bones, causing an injury and rupture of the muscle fibres and blood vessels. The rupture usually occurs deep in the muscle. In other cases the bleeding can occur after a larger or minor rupture of a muscle on the front of the upper arm or rupture of a muscle on the back of the upper arm. The bleeding can either penetrate the muscle membrane and spread over a large area or it can accumulate in the muscle.
Symptoms: Pain and swelling in the muscle. In some cases a hard, tender accumulation (accumulated bleeding in the muscle) can be felt. In other cases a bluish discolouration of the subcutis (the bleeding has penetrated the muscle membrane and spread into the subcutis) occurs after a few days. The pain is aggravated upon activation and stretching of the muscle. Acute treatment: Click here. Examination: In light cases with only minimal tenderness and no discomfort when walking normally, medical examination is not necessarily required. Although the extent of the pain is not always a measure of the extent of the injury. In cases of more pronounced pain or difficulty using the arm, medical examination is required to ensure the correct diagnosis and treatment. Ultrasound is the most suited examination to ensure the diagnosis (Ultrasonic image). The larger the bleeding, as revealed in the ultrasound scan, the longer the healing process. Treatment: The treatment involves relief and rehabilitation as with a rupture of a muscle on the front of the upper arm or rupture of a muscle on the back of the upper arm, depending on whether the bleeding is located on the front or the back of the upper arm. In large bleedings the accumulated blood can be drained under ultrasound guidance. Some recommend treatment with rheumatic medicine (NSAID) and advise caution with regard to massage to reduce the risk of calcification in the muscle (myositis ossificans) . Complications: If progress is not smooth, you should be (re)examined and consider if the diagnosis is correct or whether complications to the muscle bleeding have added. |