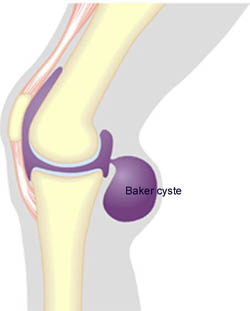
SYNOVIAL FLUID IN THE POPLITEAL SPACE
|
||
 |
||
| Cause: Injuries in the knee that bring about inflammation of the synovial membrane (synovitis), causing formation of an excess of synovial fluid in the knee. The fluid is pressed out through the joint-capsule and accumulates in the popliteal space (Baker cyst). The Baker cyst is consequently a symptom of something not right in the knee. The connection from the joint to the Baker cyst can in some cases become strangulated, meaning that the Baker cyst can still be present even thought he injury in the knee has healed.
Symptoms: A sensation of the popliteal space being filled up, and difficulty in flexing the knee completely. There is often also discomfort from the changes in the knee that provoked the Baker cyst. Examination: As the presence of a Baker cyst is usually a symptom of an injury in the knee, anyone with a Baker cyst or discomfort in the knee should undergo a medical examination. It will often prove difficult to diagnose even a large Baker cyst from a normal examination, and the diagnosis is made easiest and swiftest from an ultrasound scan (Ultrasonic image). Treatment: Treatment is naturally dependant upon the injury in the knee joint that has provoked the Baker cyst. The accumulation in the knee and the Baker cyst can be treated with rheumatic medicine (NSAID) or more effectively by injection of corticosteroid in the knee (or the Baker cyst), preceded by draining of the fluid which can advantageously be performed under ultrasound guidance. Synovial fluid can be drained from the Baker cyst if there is a connection between the knee joint and the Baker cyst, and ultrasound scanning will show the injected corticosteroid spread through the knee joint as well as the Baker cyst (article). The content of the Baker cyst is often quite thick (gelatinous) if the Baker cyst does not communicate with the knee joint. Rehabilitation: Treatment is completely dependant upon the provoking cause of the Baker cyst. Complications: If smooth progress is not achieved, it should be considered whether the diagnosis is correct. Amongst others, the following should be considered:
The bursa can become infected with bacteria in rare cases. This is a serious condition where the bursa becomes red, warm and increasingly swollen and tender. This condition requires immediate medical examination and treatment. If relief and medicinal treatment (including ultrasound guided injection of corticosteroid) does not produce any progress, a surgical removal of the bursa can be attempted. |
