|
Iliopsoas bursa imaging: efficacy in depicting abnormal iliopsoas tendon motionin patients with internal snapping hip syndrome. MATERIALS AND METHODS. RESULTS. CONCLUSION. |
Kategoriarkiv: Bursitis on the front of the hip joint
examination-article
|
Iliopsoas bursitis and tendinitis. A review. |
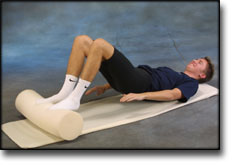
step4
Training ladder for:
BURSITIS ON THE FRONT OF THE HIP JOINT
(BURSITIS ILIOPECTINEA)
STEP 4 |
Unlimited: Cycling. Swimming. Running on a smooth surface.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
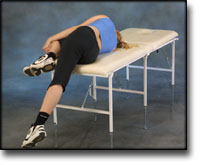
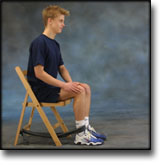
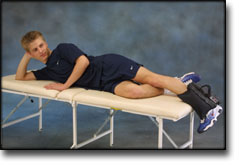
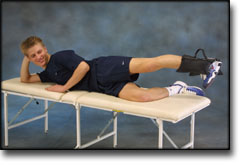
Stretching is carried out in the following way: stretch the muscle group for 3-5 seconds. Relax for 3-5 seconds. The muscle group should subsequently be stretched for 20 seconds. The muscle is allowed to be tender, but must not hurt. Relax for 20 seconds, after which the procedure can be repeated. The time consumed for stretching, coordination and strength training can be altered depending on the training opportunities available and individual requirements. |
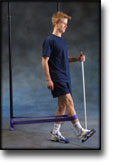
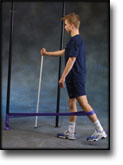
step3
Training ladder for:
BURSITIS ON THE FRONT OF THE HIP JOINT
(BURSITIS ILIOPECTINEA)
STEP 3 |
Unlimited: Cycling. Swimming. Light running on a smooth surface.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Stretching is carried out in the following way: stretch the muscle group for 3-5 seconds. Relax for 3-5 seconds. The muscle group should subsequently be stretched for 20 seconds. The muscle is allowed to be tender, but must not hurt. Relax for 20 seconds, after which the procedure can be repeated. The time consumed for stretching, coordination and strength training can be altered depending on the training opportunities available and individual requirements. |
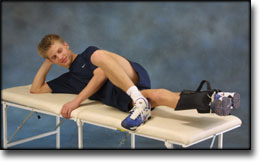
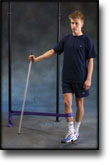
step2
Training ladder for:
BURSITIS ON THE FRONT OF THE HIP JOINT
(BURSITIS ILIOPECTINEA)
STEP 2 |
Unlimited: Gentle cycling with a low load. Swimming. Jogging on a soft surface.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Stretching is carried out in the following way: stretch the muscle group for 3-5 seconds. Relax for 3-5 seconds. The muscle group should subsequently be stretched for 20 seconds. The muscle is allowed to be tender, but must not hurt. Relax for 20 seconds, after which the procedure can be repeated. The time consumed for stretching, coordination and strength training can be altered depending on the training opportunities available and individual requirements. |
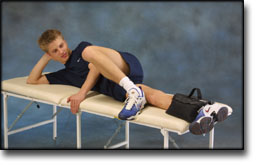
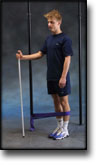
step1
Training ladder for:
BURSITIS ON THE FRONT OF THE HIP JOINT
(BURSITIS ILIOPECTINEA)
STEP 1 |
| The indications of time after stretching, coordination training and strength training show the division of time for the respective type of training when training for a period of one hour. The time indications are therefore not a definition of the daily training needs, as the daily training is determined on an individual basis.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Stretching is carried out in the following way: stretch the muscle group for 3-5 seconds. Relax for 3-5 seconds. The muscle group should subsequently be stretched for 20 seconds. The muscle is allowed to be tender, but must not hurt. Relax for 20 seconds, after which the procedure can be repeated. The time consumed for stretching, coordination and strength training can be altered depending on the training opportunities available and individual requirements. |