INFLAMMATION OF THE TENDON SHEATH
|
||
|
||
|
||
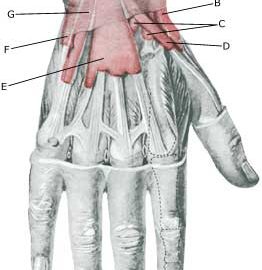
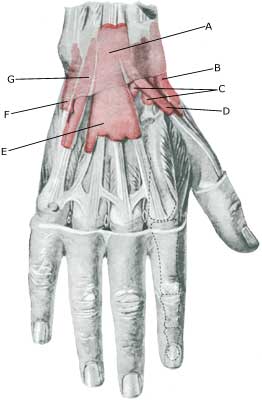
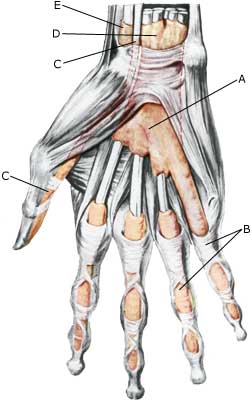
| Cause: Tenosynovitis occurs due to mechanical irritation of the tendon sheath following repeated uniform movements of the tendon, causing the tendon to become inflamed, swollen and sometimes crepitate upon movement (article 1). In some cases long-term inflammation of the tendon sheath can cause a weakening and in the worst cases a rupture of the tendon (article 2).
Symptoms: Pain along the tendon sheath, which can sometimes feel swollen and crepitating upon movement. Acute treatment: Click here. Examination: Slight cases do not necessarily require medical examination. The doctor should be consulted if there is lack of progress despite relief. The diagnosis is usually made from a normal medical examination, however, in the event of doubt in connection with the diagnosis an ultrasound scan can be performed which will easily and quickly detect the inflammation (article), (Ultrasonic image). Treatment: Relief from the triggering load factor. In case of lack of progress with relief, a medical treatment in the form of rheumatic medicine (NSAID) or the injection of corticosteroidi in the tendon sheath can be considered. Since the effect and the risk is dependant on the injection being done correctly, it can advantageously be performed with ultrasound guidance. Rehabilitation: Usually fitness training in the form of cycling, running and rehabilitation according to the guidelines under rehabilitation, general can be started immediately. Bandage: With many tenosynovitis cases a support splint can be used to advantage as needs require. Complications: Lengthy periods of tenosynovitis can cause damage to the tendon resulting in a rupture of the tendon, following which the functions of the fingers (stretching, bending) can suddenly be lost. |