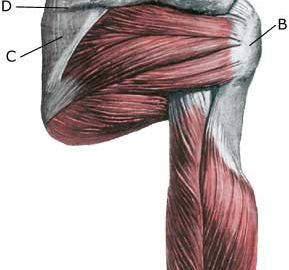
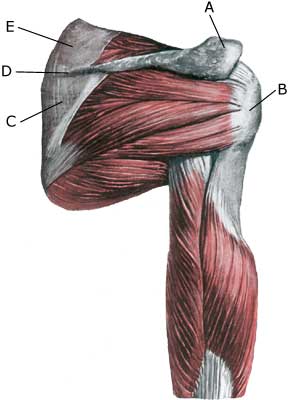
Anatomy: Four muscles are part of the rotator cuff surrounding the shoulder joint, and controls, coordinates and assists movement of the shoulder: M supraspinatus (the upper shoulder blade muscle), M infraspinatus, M subscapularis and M teres minor. When the arm is moved away from the body and above the head (abducated) the supraspinatus muscle slips under the upper bone projection of the shoulder blade (acromion). |
||
|
||
|
Cause: In case of repeated loads with the arm above the head (tennis, swimming) the upper shoulder blade muscle tendon (M supraspinatus) become inflamed swells and may become squeezed between the head of the upper arm (caput humeri) and the upper bone projection of the shoulder blade (acromion). Additionally this causes fraying and weakening of the tendon with risk of ruptures. It is not uncommon for tendinitis to be seen in conjunction with inflammation of the bursa (bursitis subacromialis). Acute treatment: Click here. Treatment: The treatment primarily involves relief from the pain inducing activities, stretching and rehabilitation of the muscles around the shoulder. If lack of progress in rehabilitation a medical treatment in the form of rheumatic medicine (NSAID) or injection of corticosteroid (usually in the bursa above the supraspinatus muscle) may be considered. Since the injection of corticosteroid is part of a long-term rehabilitation of a long-term injury, it is often necessary that the rehabilitation period stretches over several weeks to months, to reduce the risk of recurrences and ruptures. Naturally the tendon can not sustain maximum load after only a short rehabilitation period. If calcification is present in the shoulder muscle, an attempt may be made to extract this at the same time corticosteroid is injected around the calcification (article). The optimal effect at minimal risk can be accomplished by performing the injections guided by ultrasound. The wrong structures are hit in more than half the cases where the injection is done blindly (article). In lack of progress with rehabilitation and medical treatment a surgical treatment can be attempted. Complications: If smooth progress is not achieved, it should be considered whether the diagnosis is correct or whether complications have arisen. Amongst others the following should be considered:
|