|
||
|
||
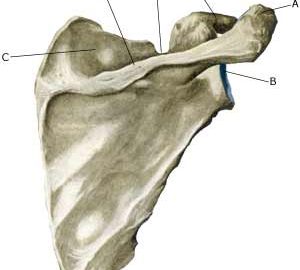
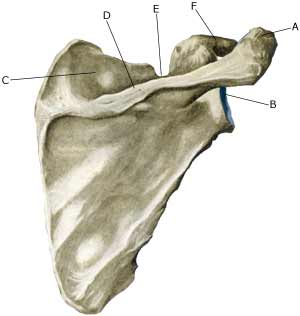
| Cause: In case of repeated strain with movement in the shoulder joint, an entrapment of the nerve (article). Entrapment of the nerve may also occur as the result of a blow.
Symptoms: Usually a burning or cutting pain in the shoulder. Possibly a sense of weakness in the shoulder. In case of long-term symptoms degradation of the shoulder blade muscles will occur. Examination: Uncharacteristic shoulder symptoms, not improved by relief, should be examined by a physician. If the results of the examination indicate nerve entrapment the diagnosis is made by a nerve conduction velocity test (EMG). Treatment: The treatment involves relief from the pain inducing activity, stretching and rehabilitation of the muscles around the shoulder. If no progress is made with relief and rehabilitation, surgical intervention may be attempted (article-1) (article-2). Relief is the primary element, and it is particularly important that the rehabilitation does not cause any discomfort. Fitness training should not be resumed until the pain has stopped Complications: If satisfactory progress is not made, a physician should be consulted to ensure that the diagnosis is correct and that no complications have arisen. Amongst others the following should be considered:
|