

|
||
|
||
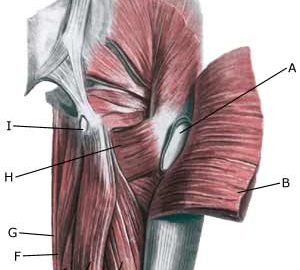
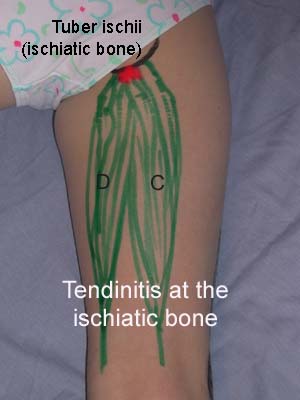
| Cause: Inflammation of the tendon fastenings (tendinitis) at the ischiatic bone (tuber ischiadicum) occurs following repeated uniform (over)loads (e.g. running, sprinting) causing microscopic ruptures in the tendon, and especially at the tendon fastening. Tendinitis is a warning that the training performed is too strenuous for the muscles in question, and if the load is not reduced a rupture of the posterior thigh muscle fastening on the ischiatic bone (“pulled muscle”) may occur. This will result in a considerably prolonged rehabilitation period.
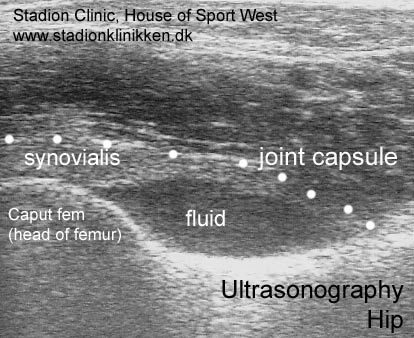
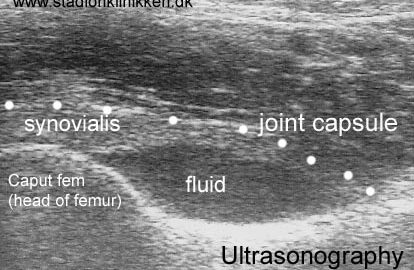
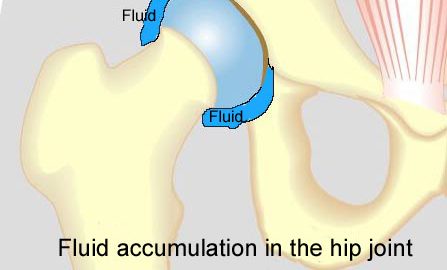
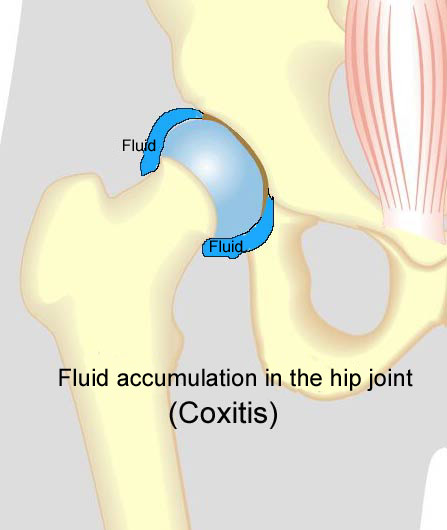
Symptoms: Pain in the ischiatic bone can occasionally radiate down into the rear of the thigh. The pain is aggravated when applying pressure on the bone (e.g. sitting position), stretching and activating the posterior thigh muscles (flexing the knee against resistance). Acute treatment: Click here. Examination: In slight cases with only minimal tenderness and no discomfort with walking, medical examination is not necessarily required. The extent of the tenderness is, however, not always a mark of the degree of the injury. In cases of more pronounced pain or tenderness, medical examination is required to ensure the correct diagnosis and treatment. The diagnosis is usually made on the basis of a normal medical examination, however, if there is any doubt concerning the diagnosis, this can be confirmed by ultrasound scanning or MR scanning (article). Treatment: The treatment usually comprises relief, stretching and rehabilitation (article). If the rehabilitation does not progress satisfactorily, medicinal treatment in the form of rheumatic medicine (NSAID) can be considered, or corticosteroid injection in the area surrounding the inflamed tendon fastening on the ischiatic bone. As the injection of corticosteroid is always an element in the long term rehabilitation of a very serious, chronic injury, it is vital that the rehabilitation period lasts over several months in order to reduce the risk of a relapse or ruptures. The tendon can naturally not sustain maximal load after a long-term injury period and only a short-term rehabilitation period. If the diagnosis is made by use of ultrasound scanning, the injections are performed under guidance of ultrasound, and the rehabilitation is progressed in accordance with the guidelines mentioned, then the treatment involving corticosteroid injections has very few risks connected. If satisfactory progress is not made following the rehabilitation and medicinal treatment, surgical intervention can be considered. Long-term results of operations are often disappointing, despite publication of a minor series with good results (article). Complications: If the treatment does not progress according to plan, it should be considered if the diagnosis is correct or whether complications have arisen. The following should in particular be considered:
|
|
||
|
||
|
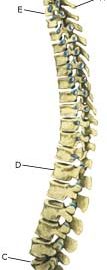
Cause: Scheuermann’s disease occurring in approximately 4% of the population (article). A curvature of the back occurs (bending over forwards) due to the vertebrae becoming wedge shaped. There are also characteristic x-ray finds. The cause of the condition is unknown, but evidence tends to suggest that the condition is hereditary (article). Symptoms: Back curvature localised high in the back (thoracal Scheuermann) gives often only few, if any, symptoms. Back curvature localised in the lower back (thoracolumbal or lumbal Scheuermann) does entail back pain for the majority (article). Treatment: The vast majority of cases can be treated with training, attempting to maintain the mobility of the back, counteract the curvature tendency and strengthen the stomach and back muscles. A corset can in some cases be used until the young person is fully grown. An operation can be performed only in very rare cases. The condition has a good prognosis (article), and even after an operation it is still possible to take part in many different forms of sport (article). Complications: In some cases a crooked back can have other causes (infection, nerve disease, inborn bone change, rheumatic illness, bone disease, metabolic disorder). |
|
Apophyseal injuries in the young athlete. |
|
Hamstring strains in athletes: diagnosis and treatment. |
|
Hamstring injuries. Current trends in treatment and prevention. |

|
Ischial tuberosity apophysitis and avulsion among athletes.
|