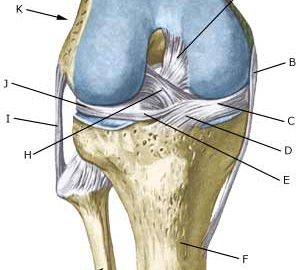
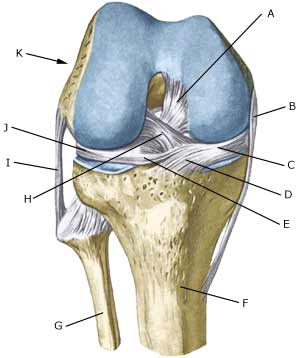
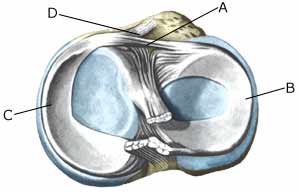
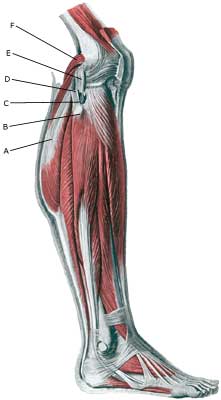
Cause: The mucous fold will become inflamed if an entrapment of the fold occurs, or if the fold suffers internal bleeding. This will result in thickening and subsequently cause pain. Symptoms: The mucous fold in the inner joint chamber (medial plica) will most often give symptoms which are difficult to distinguish from the symptoms of a meniscus lesion. The pain is usually localised on the inner side of the knee cap, in front of the inner joint line. The pain often occurs quite suddenly following certain movements, and can be accompanied by swelling in the knee. The knee can lock if a flap of the mucous fold becomes entrapped (article). Examination: A medical examination is always necessary to ensure the diagnosis if there is any suspicion of an inflamed mucous fold in the knee. A tender string inside the knee cap can occasionally give a slipping sensation, but often a normal clinical examination is not sufficient. It is often necessary to perform an arthroscopic examination (telescopic examination of the joint) or MR-scan to make the diagnosis (article). Treatment: Treatment comprises relief and careful rehabilitation of the knee. If the discomfort does not slowly diminish, the treatment can be supplemented with rheumatic medicine (NSAID) or injection of corticosteroidi in the mucous fold. Medial synovial shelf plica syndrome. Treatment by intraplical steroid injection. If this does not give the desired results, the mucous fold can be removed by arthroscopy (telescopic examination of the knee). Exerting load on the knee can commence as soon as the pain and swelling in the knee has diminished. In the best cases, full activity is possible after a period of a few weeks. In uncomplicated cases, it should be possible to resume a full level of sports activity during the course of a month. Rehabilitation must not be allowed to cause increased swelling (or pain) in the knee. Complications: If insufficient progress is made prior to an operation it must be considered if the diagnosis is correct. Supplementary examinations will often be required (X-ray, ultrasound or MR scan). In particular the following should be considered:
Following an arthroscopic examination fluid accumulation in the joint (traumatic arthritis/synovitis), should be considered, as well as infection in the scar or knee joint, which will always require medical attention as soon as possible. |